Weiss Technik Academy
Trainings & Workshops - Benefit from our know-how.
Learn more
The right support for your shock tests - vertical or damper shock
In order to be able to detect latent weak points within a very short time, an ordinary temperature test is often not sufficient; shock testing is a test in which the samples are shocked. Shocking refers to temperature and means that a test specimen undergoes a very rapid temperature change between two temperature extremes - The test specimen is subjected to an abrupt temperature change. In this process, the air (or liquid) is preconditioned. That means you need a hot chamber and a cold chamber.
Both the ShockEvent D (damper shock) and ShockEvent T (vertical shock) series use air-to-air shock. In addition, weisstechnik offers “liquid-air” media, ice water shock testers as well as surge water testers.
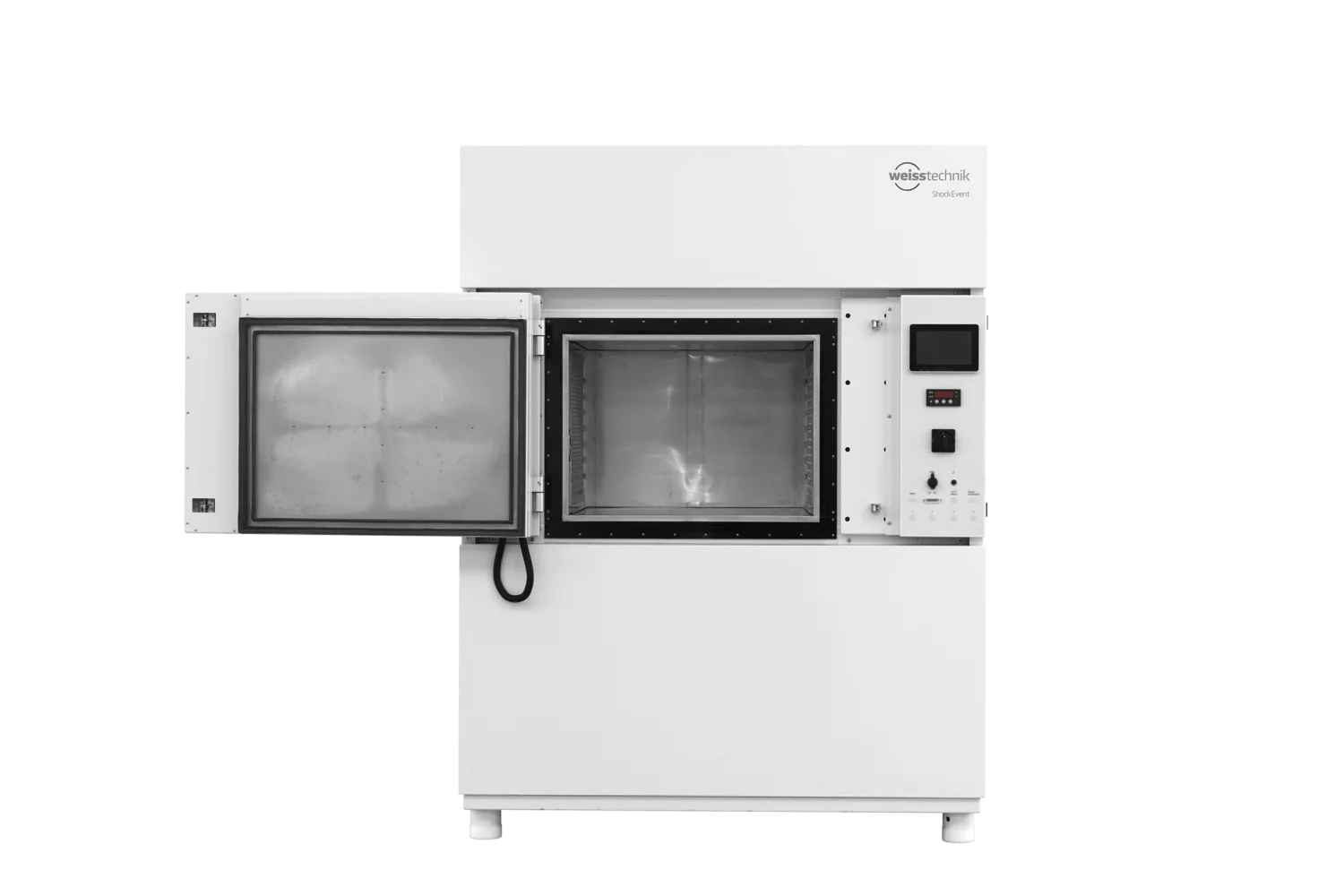
ShockEvent T is a dual-chamber vertical shock. It compresses the “transfer zone” between the cold and hot zones with a transfer time. Between these two chambers, a basket with the test material moves at a certain speed. The time it takes to move the basket is the transfer time.
In short, between the hot and cold chambers, it allows endurance tests of over 1,000 cycles to be run without defrosting. All thermal shock test chambers use R449A refrigerant, making testing future-proof for you, as well as highly environmentally and service friendly.

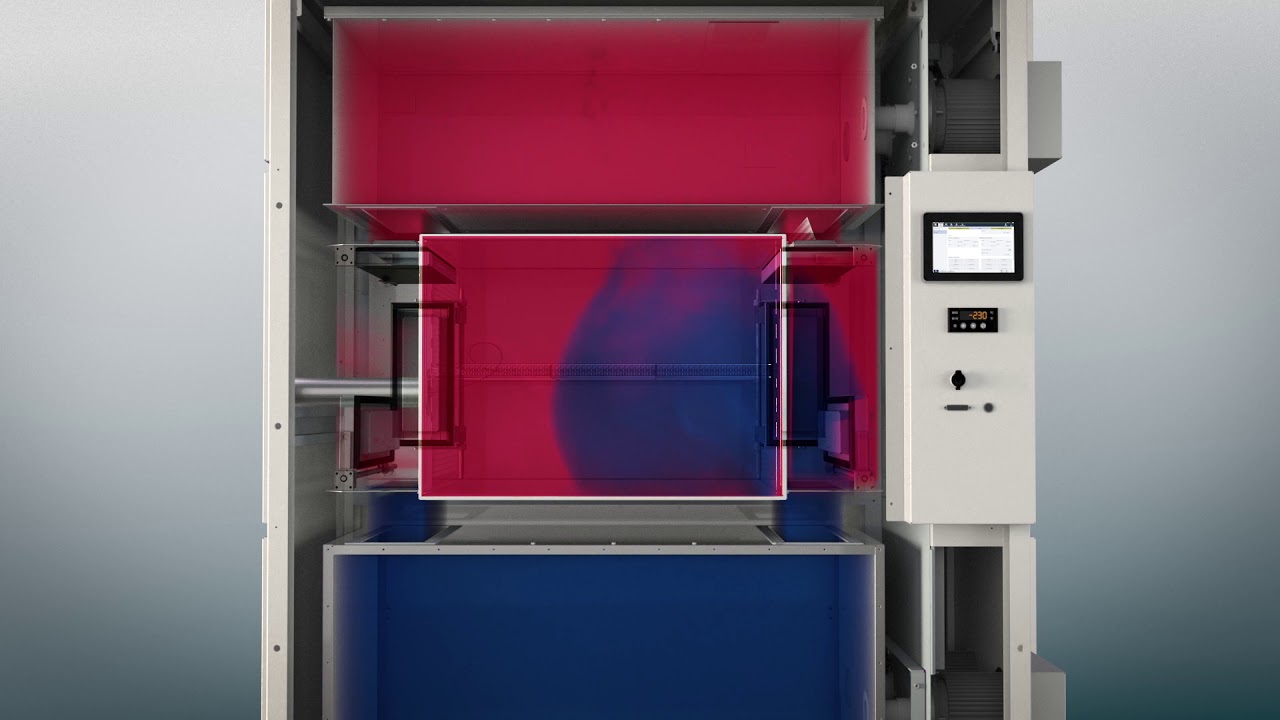
The damper shock test devices (ShockEvent D) are predestined for vibration-sensitive or active test material. The special feature of a damper shock is the fixed test space. Tempered hot and cold air is generated in chambers above and below the test chamber. The user allows this to flow to the test material via flaps.
This distinguishes it significantly from horizontal shock and vertical shock test chambers, in which the test specimen is moved between two temperature chambers within a test basket.


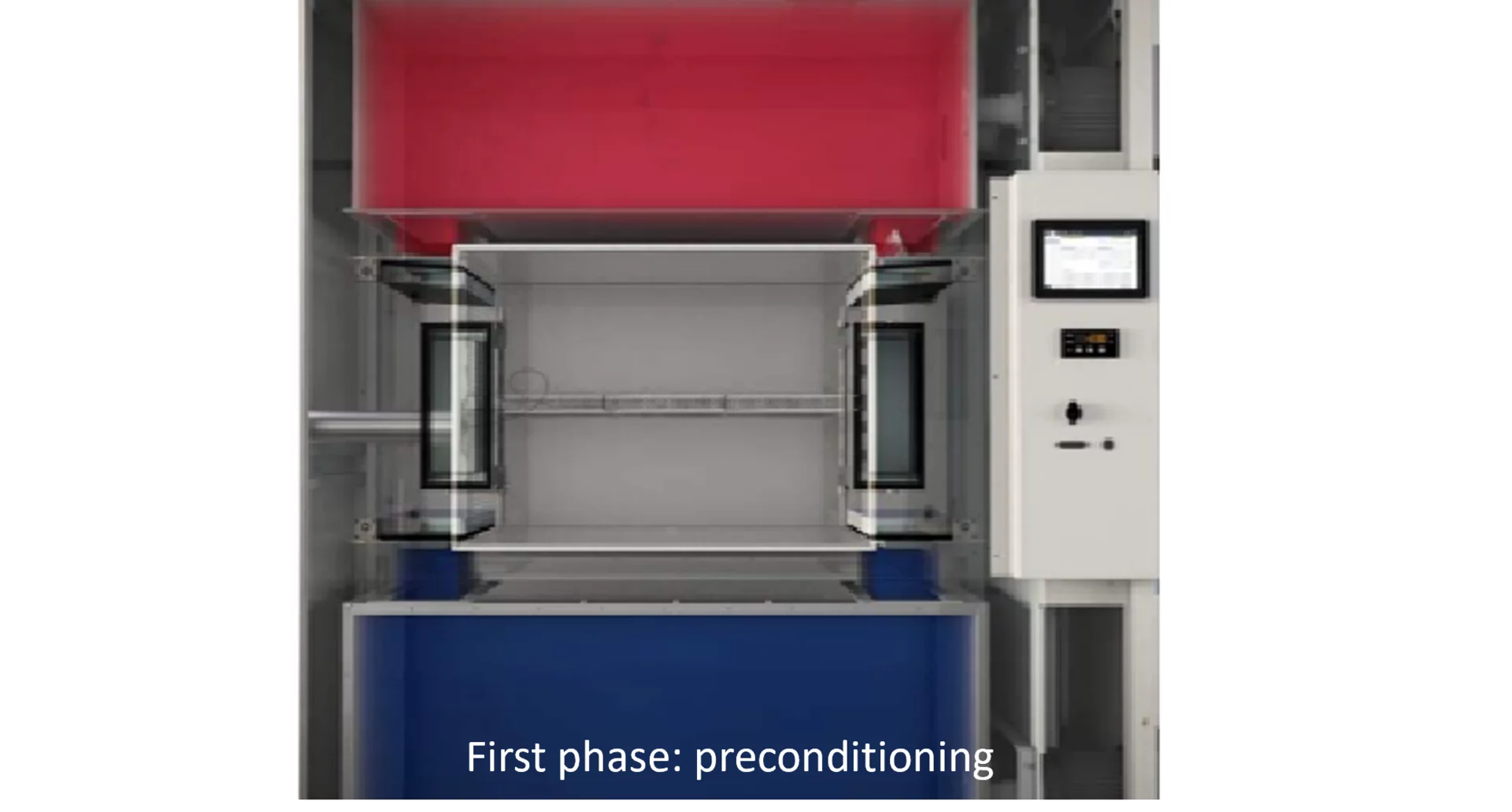
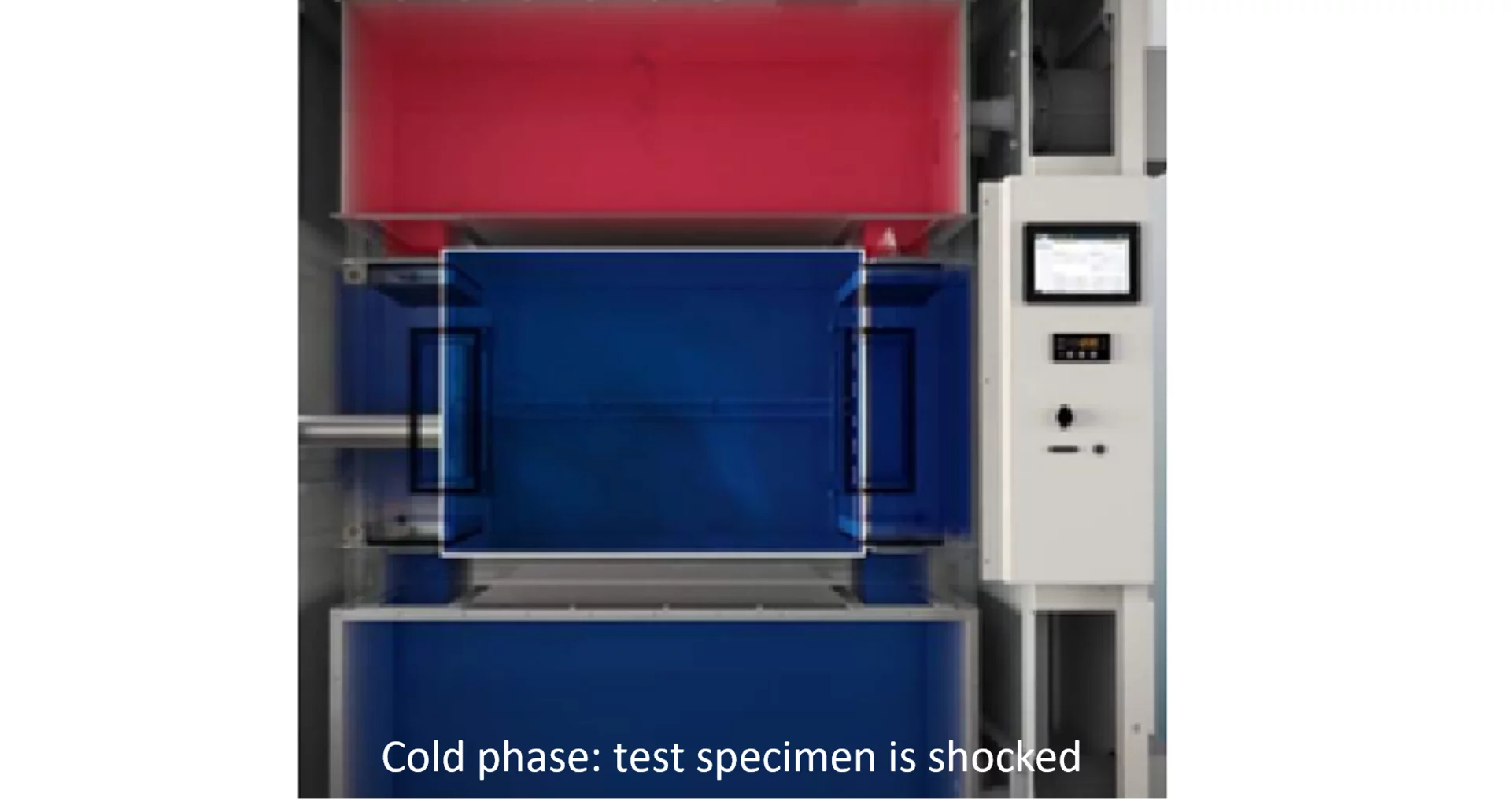
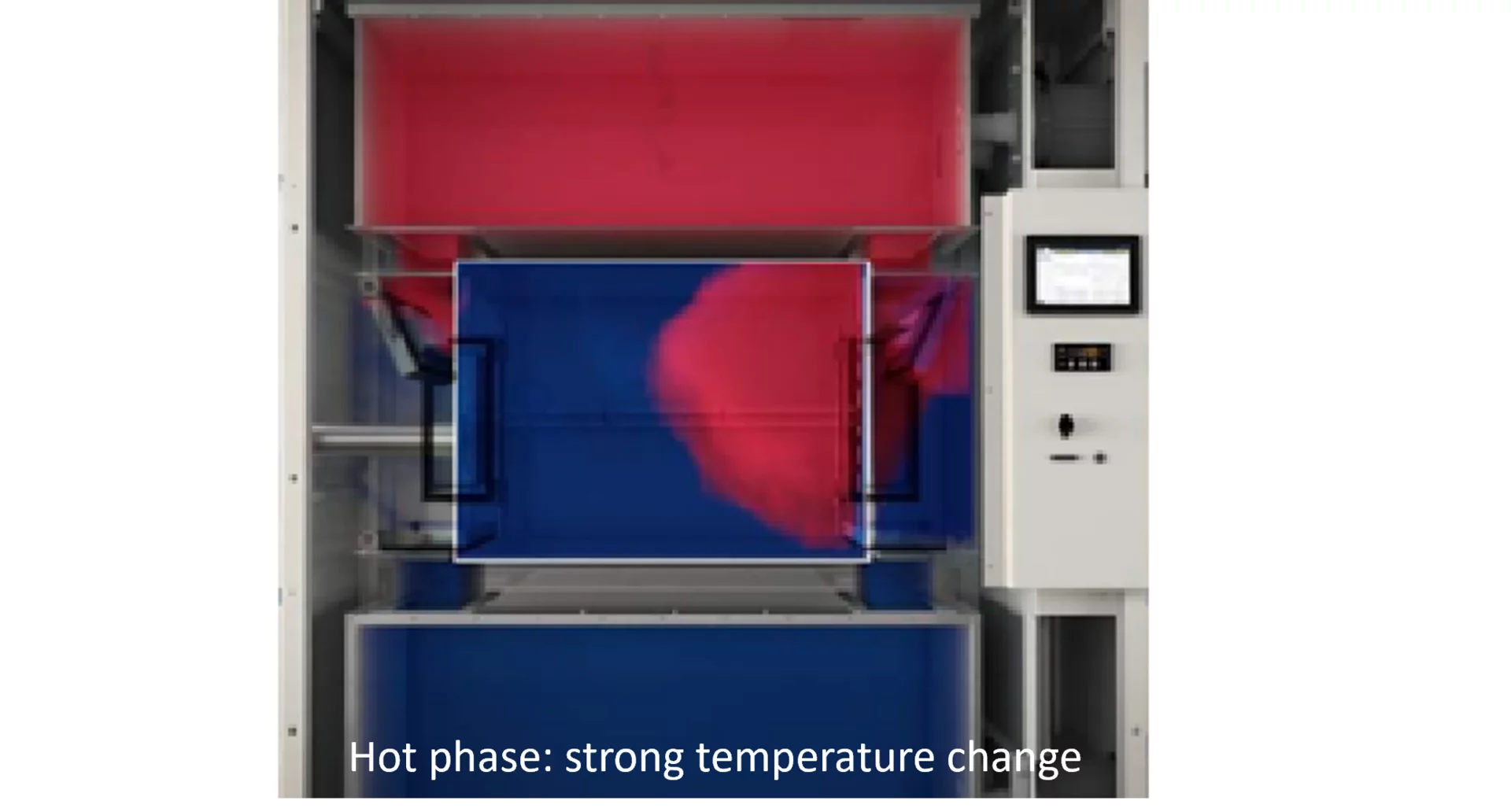
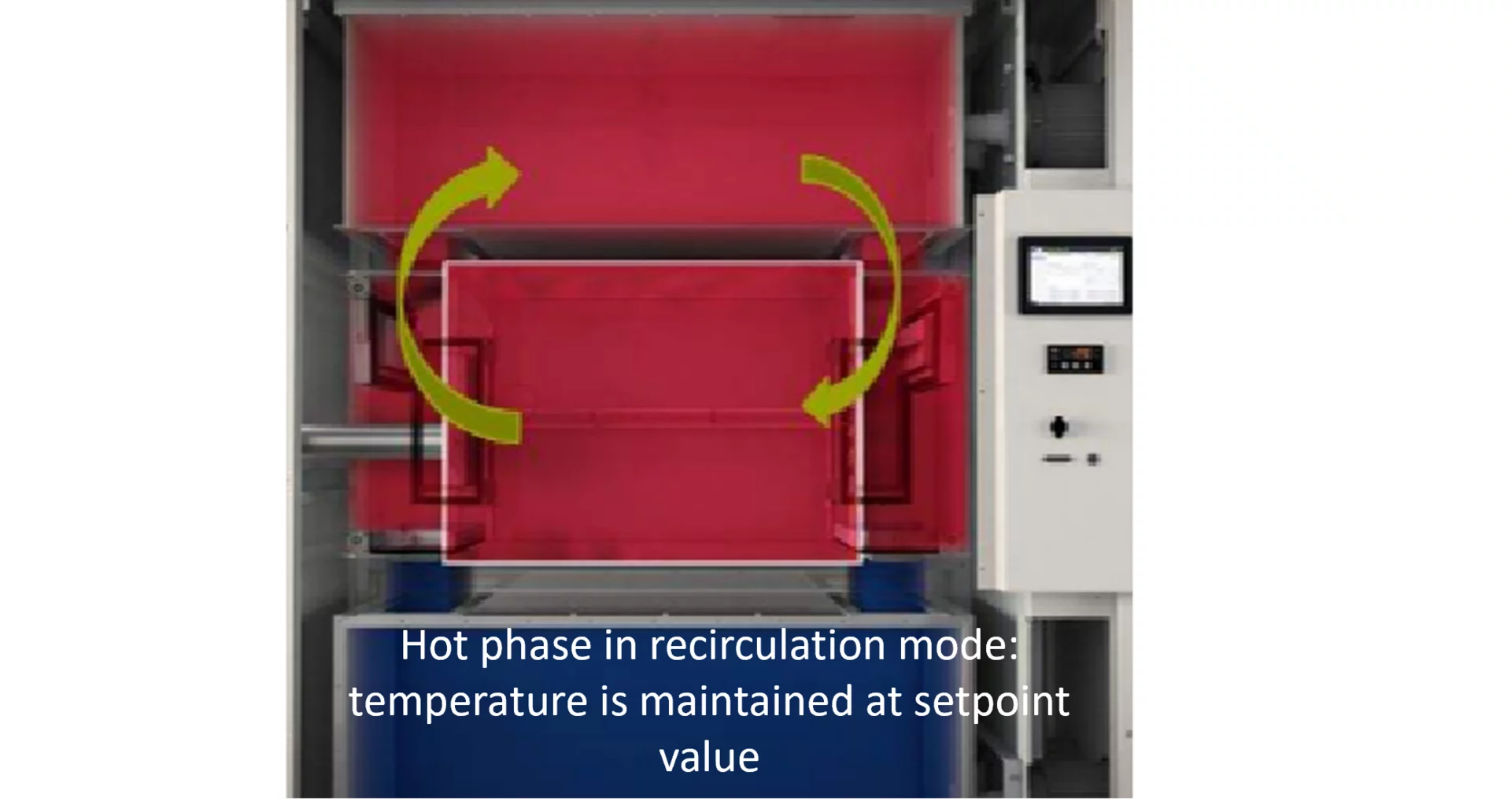
ShockEvent D also has a cold and a hot chamber. However, these only serve to precondition the air. During a test, we refer to a hot phase and a cold phase (in 2-zone mode).
Optionally, a third test phase can be added – The fresh air phase. For this purpose, the third pair of flaps is opened and ambient air flows into the test chamber.
First phase: air is preconditioned in respective chamber
Cold phase: Flaps to the cold chamber are opened – test specimen is shocked.
Hot phase: Flaps of the cold chamber close and flaps of the hot chamber open - A strong temperature change occurs.
Hot phase in recirculation mode: After the initial temperature change, the test chamber is conditioned for the remaining time in recirculation mode – temperature is maintained at the setpoint.
Optional 3-zone test: Optionally add third test phase – The fresh air phase, during which a third pair of flaps is opened and ambient air flows into test space.